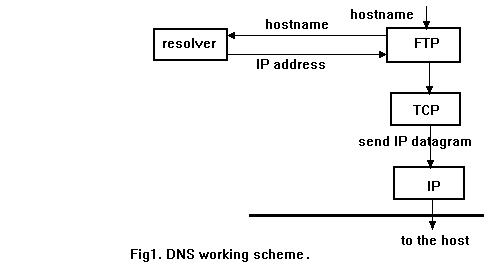
DNS, or Domain Name System, is a fundamental component of the internet that translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to access websites and other resources using familiar names rather than numeric IP addresses.
The need for DNS arises from the fact that computers on the internet communicate with each other using IP addresses, which are numerical identifiers associated with each device. However, remembering and using IP addresses for every website or online resource would be impractical for users. This is where DNS comes in, providing a hierarchical and distributed system to map domain names to IP addresses.
Here's a brief explanation of how DNS works:
-
User Enters a Domain Name: When a user enters a domain name (e.g., www.example.com) into their web browser, a request is initiated to resolve that domain to an IP address.
-
Local DNS Resolver: The user's device first checks its local DNS resolver cache to see if it already has the IP address for the requested domain. If the information is not found or has expired, the resolver proceeds to the next step.
-
Recursive DNS Server: The local DNS resolver queries a recursive DNS server. Recursive DNS servers are responsible for resolving domain names by interacting with other DNS servers to find the correct IP address.
-
Root DNS Server: If the recursive DNS server doesn't have the IP address information, it contacts one of the 13 root DNS servers. These servers hold information about the top-level domain (TLD) name servers.
-
TLD Name Server: The root DNS server directs the recursive server to the TLD name server responsible for the specific domain extension (e.g., .com, .org). The TLD name server stores information about the authoritative name servers for the requested domain.
-
Authoritative DNS Server: The TLD name server then directs the recursive server to the authoritative DNS server for the requested domain. This server holds the specific IP address associated with the domain.
-
IP Address Resolution: The authoritative DNS server provides the IP address to the recursive server, which, in turn, stores the information in its cache and returns the IP address to the user's device.
-
Accessing the Website: Now armed with the IP address, the user's device can establish a connection to the desired web server, and the requested web page is delivered to the user's browser.
DNS operates in the background, making internet usage more user-friendly by allowing people to access websites using easy-to-remember domain names while the system efficiently translates those names into the corresponding IP addresses required for actual communication between devices on the internet.